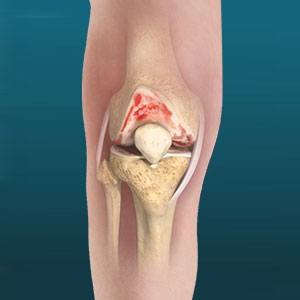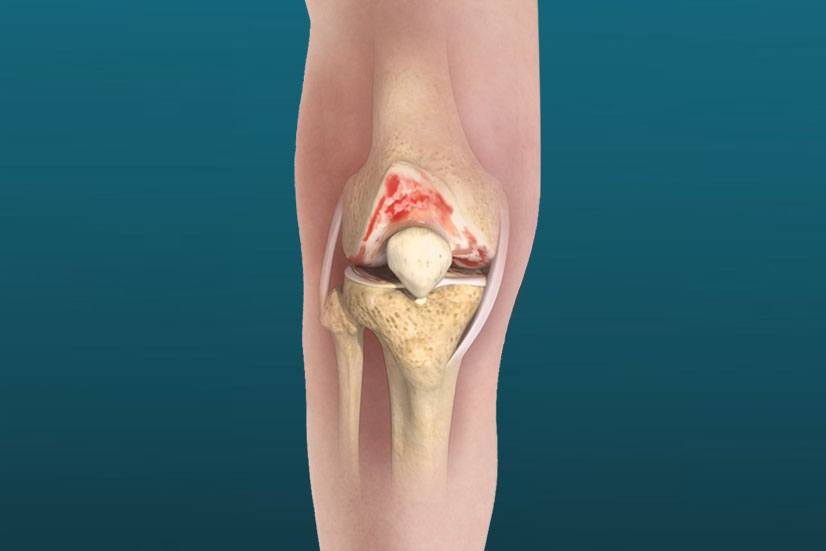
Total knee replacement (TKR), also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves replacing the damaged or worn-out surfaces of the knee joint with artificial components. This procedure is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to relieve pain or improve mobility. Understanding the conditions that may necessitate TKR and the benefits of the procedure is crucial for patients considering this life-changing surgery.
Conditions Leading to Total Knee Replacement
Several conditions can lead to the need for a total knee replacement. The most common include:
- Osteoarthritis (OA):
- Description: OA is the most prevalent reason for knee replacement surgery. It is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, which cushions the ends of the bones in the knee joint. As the cartilage wears away, bones begin to rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased mobility.
- Symptoms: Patients with OA often experience pain that worsens with activity, stiffness after periods of inactivity, and reduced range of motion. Over time, these symptoms can significantly impact daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and even sitting or lying down.
- Progression: As OA progresses, the pain can become constant, and the joint may become visibly deformed. When conservative treatments like physical therapy, medications, and injections no longer provide relief, TKR may be recommended.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
- Description: RA is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints, including the knee. Unlike OA, which primarily affects the cartilage, RA targets the synovium, the lining of the joint, leading to painful swelling and eventual joint damage.
- Symptoms: RA symptoms include joint pain, swelling, warmth, and stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of rest. The inflammation can also lead to joint deformity and loss of function.
- Progression: In severe cases, the destruction of cartilage and bone by the inflammatory process can lead to the need for TKR to restore function and alleviate pain.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis:
- Description: Post-traumatic arthritis occurs after a knee injury, such as a fracture, ligament tear, or meniscus injury. The trauma can damage the cartilage, leading to arthritis over time.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of post-traumatic arthritis are similar to those of OA, including pain, swelling, and stiffness. The onset of symptoms may be delayed, sometimes occurring years after the initial injury.
- Progression: If the arthritis becomes severe and affects the patient's quality of life, TKR may be necessary.
- Avascular Necrosis:
- Description: Avascular necrosis occurs when the blood supply to the bone is disrupted, leading to the death of bone tissue. This condition can affect the knee and lead to the collapse of the joint surface.
- Symptoms: Patients with avascular necrosis may experience pain that worsens with weight-bearing activities and progresses to constant pain as the condition worsens.
- Progression: When avascular necrosis affects the knee severely, it can result in significant joint damage, making TKR a viable option to restore function.
- Congenital or Developmental Abnormalities:
- Description: Some patients may be born with or develop abnormalities in the knee joint that predispose them to early joint degeneration.
- Symptoms: These abnormalities can lead to misalignment of the joint, causing uneven wear and tear on the cartilage, leading to pain and dysfunction.
- Progression: If these abnormalities result in severe arthritis or joint damage, TKR may be required to correct the alignment and restore normal function.
Benefits of Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is a highly successful procedure with several benefits for patients suffering from severe knee conditions:
- Pain Relief:
- Benefit: The most significant benefit of TKR is the relief from chronic knee pain. By replacing the damaged joint surfaces with artificial components, the painful bone-on-bone contact is eliminated.
- Outcome: Most patients experience a dramatic reduction in pain, allowing them to return to activities they once enjoyed.
- Improved Mobility and Function:
- Benefit: TKR can significantly improve joint function and mobility, allowing patients to perform daily activities with greater ease.
- Outcome: Patients often report better walking ability, improved ability to climb stairs, and enhanced overall movement.
- Enhanced Quality of Life:
- Benefit: The combination of pain relief and improved function can lead to a significant improvement in the overall quality of life.
- Outcome: Patients can enjoy a more active lifestyle, participate in social activities, and regain independence.
- High Success Rate:
- Benefit: TKR is one of the most successful surgeries in orthopedic medicine, with over 90% of patients reporting satisfaction with the results.
- Outcome: The prosthetic components used in TKR are designed to last for 15-20 years or more, depending on the patient’s activity level and overall health.
- Correction of Deformities:
- Benefit: TKR can correct deformities caused by arthritis or other conditions, such as bowlegs or knock-knees.
- Outcome: Restoring proper alignment not only improves the appearance of the knee but also enhances its function and reduces pain.
Total knee replacement is a life-changing procedure for many patients suffering from debilitating knee conditions. Patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options by understanding the conditions that lead to TKR and the benefits of the procedure. If you are experiencing chronic knee pain that interferes with your daily life, it may be time to consult with an orthopedic specialist to discuss whether total knee replacement is the right choice for you.
Medical References
1. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS)
2. Mayo Clinic - Knee Replacement Surgery
3. National Institutes of Health (NIH) - Knee Replacement
4. Arthritis Foundation - Total Knee Replacement